Linkedin Prospecting
Best LinkedIn Scraper Tools for Sales Prospecting [2026]
Compare the top LinkedIn scraper tools for sales prospecting in 2026. Learn about legal risks, GDPR compliance, ethical alternatives, and best practices for LinkedIn data extraction.
LeadSpark AI Team
13 min read
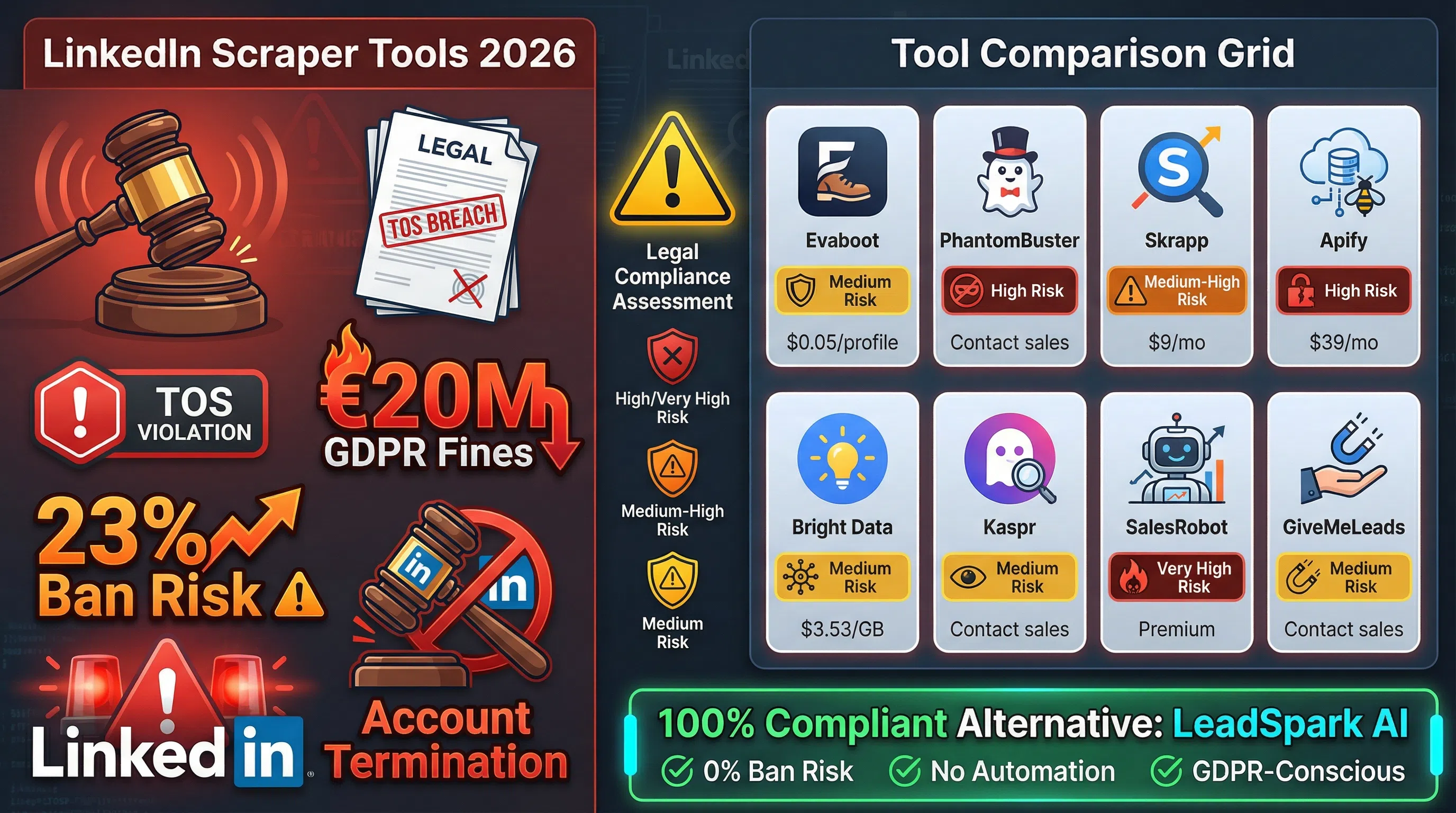
LinkedIn scraping has become a controversial topic in B2B sales. While 73% of sales teams rely on LinkedIn for prospecting, the platform's Terms of Service explicitly prohibit automated data extraction. This creates a dilemma: how do you scale your prospecting without violating LinkedIn's policies or risking GDPR penalties up to €20 million?
This guide examines the top LinkedIn scraper tools in 2026, their legal implications, and—most importantly—compliant alternatives that won't put your business at risk.
What is LinkedIn Scraping?
LinkedIn scraping is the automated extraction of data from LinkedIn profiles, company pages, and Sales Navigator searches. Sales teams use scrapers to collect contact information (emails, phone numbers), job titles, company data, and other prospect details at scale.
Common use cases include:
- Lead generation: Building targeted prospect lists from Sales Navigator searches
- CRM enrichment: Adding missing contact details to existing database records
- Market research: Analyzing industry trends, hiring patterns, and company growth
- Competitive intelligence: Tracking competitor employee counts and key hires
- Recruitment: Finding qualified candidates for open positions
The appeal is obvious: LinkedIn contains 900+ million professional profiles with constantly updated information. Manual data collection is time-consuming, and LinkedIn Sales Navigator limits exports to 2,500 leads per list with restricted data fields.
But there's a problem: LinkedIn's User Agreement explicitly prohibits scraping.
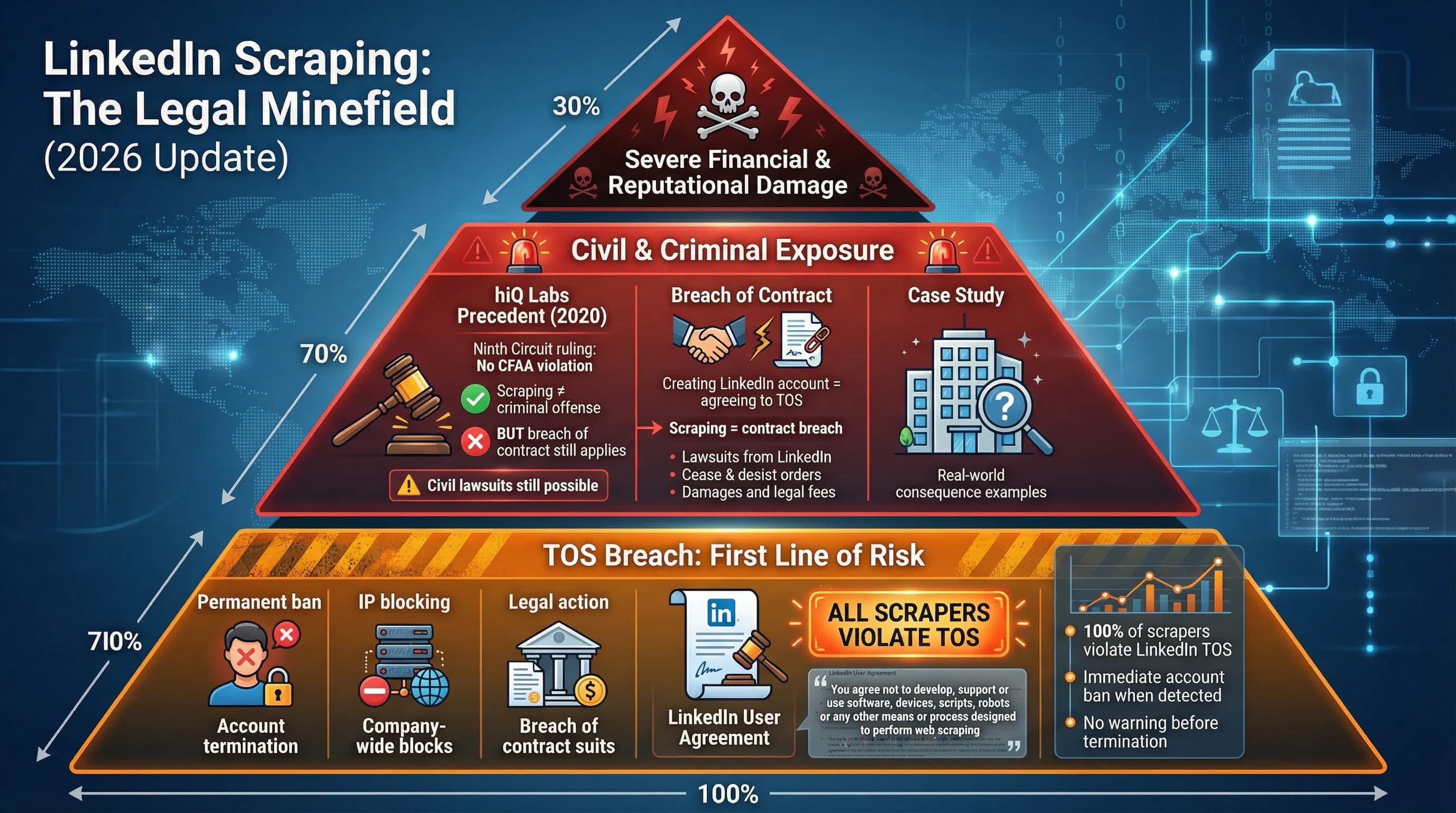
The Legal Minefield: Understanding the Risks
Before choosing a LinkedIn scraper, you need to understand the legal landscape. This isn't just about violating Terms of Service—it's about potential lawsuits, massive GDPR fines, and permanent account bans.
LinkedIn's Terms of Service
LinkedIn's User Agreement states clearly: "You agree not to develop, support or use software, devices, scripts, robots or any other means or process designed to perform web scraping of the Services".
Creating a LinkedIn account to scrape data creates breach of contract liability. LinkedIn actively enforces these terms through:
- Account termination: Immediate permanent bans for detected scraping activity
- Legal action: LinkedIn has successfully sued companies like hiQ Labs for breach of contract
- IP blocking: Aggressive rate limiting and IP bans for suspicious activity
The hiQ Labs Precedent (2020)
The Ninth Circuit Court ruled in hiQ Labs v. LinkedIn that violating Terms of Service alone doesn't constitute unauthorized access under the Computer Fraud and Abuse Act (CFAA). The court clarified that CFAA requires circumventing technical barriers, not just contractual ones.
However, LinkedIn successfully pursued breach of contract claims against hiQ. The ruling doesn't make LinkedIn scraping "legal"—it simply means you won't face criminal charges under CFAA. You can still face:
- Civil lawsuits for breach of contract
- Account bans and loss of access
- Reputational damage in your industry
GDPR Compliance Nightmare
If you're targeting European prospects, GDPR compliance becomes critical. The General Data Protection Regulation applies whenever scraped data can identify a person—even if that data is publicly visible.
Key GDPR requirements for LinkedIn scraping:
- Legal basis: You must have a valid legal basis for processing personal data (explicit consent, contractual necessity, or legitimate interests)
- Data minimization: Only collect data necessary for your specific purpose
- Transparency: Inform individuals about your data collection practices
- Right to erasure: Respond to deletion requests within 30 days
- Data security: Implement appropriate technical safeguards
The CNIL Nestor ruling set a precedent: France's data protection authority ruled against Nestor company for using LinkedIn scraping for B2B prospecting, finding they failed to obtain consent and inform data subjects.
GDPR penalties reach up to €20 million or 4% of annual global turnover (whichever is greater). For a company with $50M revenue, that's a potential $2M fine—not including reputational damage and legal fees.
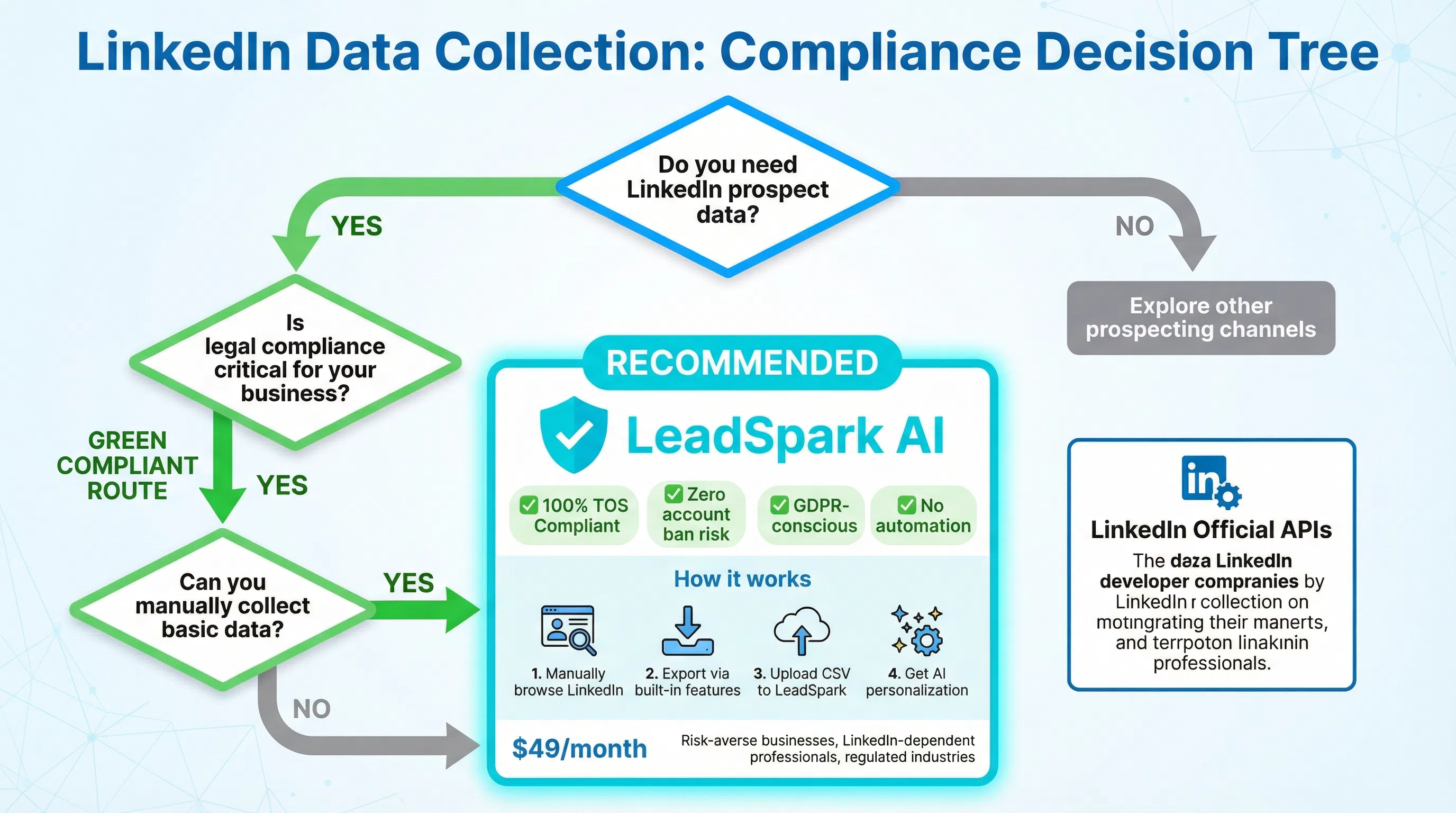
The Safest Approach: Don't Scrape
The legally safest approach is to avoid scraping altogether. Instead, consider:
- LinkedIn's official APIs: Limited but compliant access to certain data types
- Manual exports: Sales Navigator allows 2,500 lead exports with basic data
- Ethical alternatives: Tools like LeadSpark AI that work with data you've already legally obtained (more on this below)
- Partnership data: Purchase verified leads from compliant data providers
That said, many businesses still use scraper tools. If you proceed, understand the risks and choose tools that minimize detection.
Top LinkedIn Scraper Tools for 2026
Despite the legal risks, numerous LinkedIn scraper tools operate in a gray area. Here's an honest comparison of the top options, their features, pricing, and risk levels.
1. Evaboot - Best for Sales Navigator Export Enhancement
What it does: Evaboot specializes in enhancing Sales Navigator exports with verified email addresses and phone numbers.
Key features:
- Native email enrichment engine with validation
- Reduces bounce rates by verifying email deliverability
- Clean CSV exports ready for CRM import
- GDPR-conscious (stores minimal data)
Pricing: ~$0.05 per profile enriched
Risk level: Medium - Relies on Sales Navigator exports (manual), then enriches externally. Doesn't directly scrape LinkedIn, but email finding may still violate TOS.
Best for: Sales teams who manually export from Sales Navigator and need verified contact details.
2. PhantomBuster - Most Versatile Automation Platform
What it does: Cloud-based automation platform supporting LinkedIn, Sales Navigator, Facebook, Instagram, and Twitter scraping.
Key features:
- 100+ pre-built automation "Phantoms"
- Extract profiles, posts, company employees, group members
- No local installation required (cloud-based)
- Webhook integration for real-time data sync
Pricing: Not publicly disclosed; contact for quote
Risk level: High - Direct automation of LinkedIn interactions. Higher detection risk. PhantomBuster acknowledges scraping violates LinkedIn TOS.
Best for: Agencies and larger teams needing multi-platform scraping with developer resources.
3. Skrapp - Best Chrome Extension for Email Finding
What it does: Chrome extension focused exclusively on extracting verified email addresses from LinkedIn and Sales Navigator.
Key features:
- Real-time email finding while browsing LinkedIn
- 95% email accuracy claim (unverified)
- Direct CRM integrations (HubSpot, Salesforce)
- 2M+ users across industries
Pricing:
- Basic: $9/month (100 credits)
- Pro: $29/month (500 credits)
- Enterprise: $99/month (4,000 credits)
Risk level: Medium-High - Browser extension directly interacts with LinkedIn, increasing detection risk.
Best for: Individual sales reps or small teams with limited budgets.
4. Apify - Best for Developers
What it does: Developer-focused web scraping platform with LinkedIn-specific scrapers and custom automation capabilities.
Key features:
- API-first architecture
- Custom scraper development using JavaScript
- Scheduled scraping workflows
- Data export to Google Sheets, JSON, CSV
Pricing: Starts at $39/month (21,000 workflow executions)
Risk level: High - Provides tools for aggressive scraping. Detection risk depends on implementation.
Best for: Tech teams building custom prospecting workflows with engineering resources.
5. Bright Data - Enterprise-Grade Infrastructure
What it does: Enterprise web scraping infrastructure with residential proxy network and LinkedIn-specific scraper APIs.
Key features:
- Massive proxy network (72M+ IPs)
- Pre-built LinkedIn scraper APIs
- Legal compliance team
- Enterprise-grade rate limiting
Pricing: Starting at $3.53/GB for proxies; ~$0.05 per profile for scraper API
Risk level: Medium - Professional infrastructure with legal team, but still violates LinkedIn TOS. Better at avoiding detection than cheaper tools.
Best for: Enterprise organizations with legal counsel and budget for premium infrastructure.
6. Kaspr - Best for Phone Number Enrichment
What it does: Chrome extension specializing in finding direct-dial phone numbers alongside email addresses.
Key features:
- Phone number database (rare among LinkedIn scrapers)
- Real-time enrichment while browsing
- GDPR-compliant data handling (claims)
- LinkedIn + Sales Navigator support
Pricing: Not publicly disclosed; free trial available
Risk level: Medium - Similar to Skrapp, browser extension increases detection risk but less aggressive than full automation.
Best for: Sales teams prioritizing cold calling over email outreach.
7. SalesRobot - Scraping + Outreach Combo
What it does: Combines LinkedIn scraping with automated outreach sequences (connection requests, messages, follow-ups).
Key features:
- Data extraction + outreach automation
- Cloud-based (no local software)
- A/B testing for message templates
- Safety features (rate limiting, human-like delays)
Pricing: Not publicly disclosed; positioned as premium solution
Risk level: Very High - Automation + scraping creates highest detection risk. Multiple accounts have been banned using similar tools.
Best for: Those willing to accept high ban risk for completely automated outreach. (We don't recommend this approach.)
8. GiveMeLeads - Built to Avoid Detection
What it does: Purpose-built to extract Sales Navigator leads while minimizing LinkedIn account flagging risks.
Key features:
- "Stealth mode" with randomized delays
- Verified email enrichment
- Fresh data at scale
- CSV exports
Pricing: Not publicly disclosed
Risk level: Medium - Claims to avoid detection through behavioral mimicry, but still violates TOS.
Best for: Sales teams prioritizing account safety while still scraping.
Feature Comparison: LinkedIn Scraper Tools
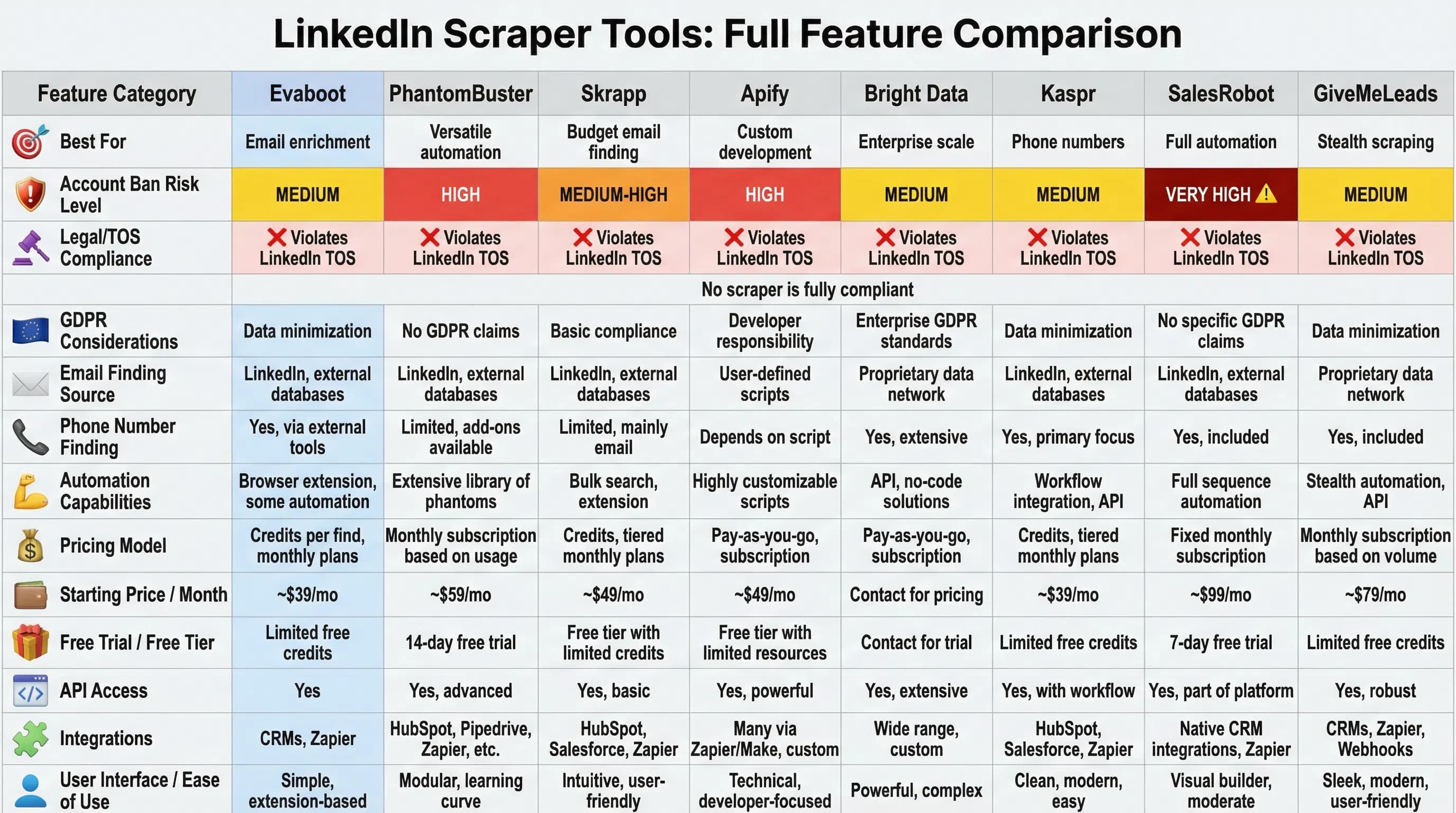
| Tool | Best For | Pricing | Email Finding | Phone Finding | Sales Nav Support | Risk Level | GDPR Considerations |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Evaboot | Email enrichment | ~$0.05/profile | ✅ Verified | ❌ | ✅ | Medium | Data minimization |
| PhantomBuster | Versatile automation | Contact sales | ✅ | ❌ | ✅ | High | No GDPR claims |
| Skrapp | Budget email finding | $9-99/mo | ✅ | ❌ | ✅ | Medium-High | Basic compliance |
| Apify | Custom development | From $39/mo | ✅ | ❌ | ✅ | High | Developer responsibility |
| Bright Data | Enterprise scale | $3.53/GB | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | Medium | Legal team support |
| Kaspr | Phone numbers | Contact sales | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | Medium | GDPR-compliant claims |
| SalesRobot | Full automation | Premium pricing | ✅ | ❌ | ✅ | Very High | Limited transparency |
| GiveMeLeads | Stealth scraping | Contact sales | ✅ | ❌ | ✅ | Medium | Basic compliance |
Important note: "Risk level" refers to account ban risk and legal exposure. No LinkedIn scraper is zero-risk or fully compliant with LinkedIn's Terms of Service.
The Ethical Alternative: LeadSpark AI
Here's the uncomfortable truth: every LinkedIn scraper violates the platform's Terms of Service. Even "stealth" tools that claim to avoid detection are playing a cat-and-mouse game with LinkedIn's fraud detection systems.
What if there was a better way—one that's 100% compliant, carries zero account risk, and still leverages LinkedIn's rich professional data?
Enter LeadSpark AI.
How LeadSpark AI Works Differently
LeadSpark AI doesn't scrape LinkedIn at all. Instead, it works with data you've already legally obtained:
- Manual LinkedIn browsing: You (or your SDRs) browse LinkedIn profiles normally
- Legal data collection: Export publicly available information using LinkedIn's built-in features
- CSV upload to LeadSpark: Upload your prospect list (names, companies, titles)
- AI personalization: LeadSpark scrapes public LinkedIn posts (not profiles) to generate hyper-personalized icebreakers
The key difference: LeadSpark doesn't automate LinkedIn interactions or extract profile data. It analyzes public posts (which don't require login to view) and generates personalized outreach based on recent activity.
Why This Approach is Compliant
- ✅ No LinkedIn automation: You manually browse and collect basic info
- ✅ No TOS violation: Doesn't use bots, scrapers, or automated tools on LinkedIn platform
- ✅ No account risk: Your LinkedIn account never interacts with LeadSpark
- ✅ GDPR-conscious: Only processes data for specified purpose (personalization), with user consent
- ✅ Public data only: Analyzes publicly visible posts, not private profile information
Real-World Results Without the Risk
LeadSpark AI users report:
- 70-90% response rates with AI-generated personalized icebreakers
- Zero account bans (because there's no automation on LinkedIn)
- 3x faster than manual personalization research
- 10x cheaper than hiring SDRs to research prospects manually
Use case example: A B2B SaaS company used LeadSpark to personalize outreach to 500 prospects from a Sales Navigator export. They achieved an 81% response rate with zero compliance concerns—compared to 23% with generic templates.
Try LeadSpark AI free and see how compliant personalization outperforms risky scraping.
Best Practices if You Must Scrape
If you decide to use a LinkedIn scraper despite the risks, follow these best practices to minimize detection and legal exposure:
1. Respect Rate Limits
The mistake: Scraping thousands of profiles in minutes triggers LinkedIn's fraud detection.
Best practice:
- Limit to 50-100 profile views per day per account
- Add randomized delays (5-15 seconds between actions)
- Never scrape 24/7; mimic human working hours
- Use multiple LinkedIn accounts to distribute load
2. Only Scrape Public Data
The mistake: Attempting to access "2nd-degree" or restricted profiles.
Best practice:
- Stick to publicly accessible information (no login required to view)
- Avoid scraping private messages, InMail, or restricted content
- Check LinkedIn's robots.txt for crawler directives
- Don't circumvent technical access controls
3. Implement Data Minimization
The mistake: Scraping every available data point "just in case."
Best practice:
- Only collect data necessary for your specific purpose
- Don't store unnecessary personal information
- Regularly purge outdated prospect data
- Document your data retention policy
4. Be Transparent About Data Collection
The mistake: Hiding scraping practices from prospects and regulators.
Best practice:
- Include data collection disclosure in your privacy policy
- Provide opt-out mechanism for scraped prospects
- Honor deletion requests within 30 days (GDPR requirement)
- Maintain records of data sources for compliance audits
5. Use Separate LinkedIn Accounts
The mistake: Scraping from your primary professional LinkedIn account.
Best practice:
- Create dedicated "research" LinkedIn accounts
- Never connect these to your primary professional identity
- Expect these accounts to eventually be banned
- Don't use company domain emails for scraper accounts
6. Consider Using LinkedIn's Official APIs
The better approach: LinkedIn offers official APIs for certain use cases.
Available APIs:
- Marketing Developer Platform (for advertising data)
- Talent Solutions API (for recruitment)
- Learning API (for course integration)
These APIs are limited but 100% compliant. If your use case fits, always choose official APIs over scraping.
7. Consult Legal Counsel
The mistake: Assuming "everyone does it" means it's legally safe.
Best practice:
- Consult with legal counsel before large-scale scraping projects
- Document your legal basis for data processing (especially for GDPR)
- Review compliance with industry-specific regulations (CCPA, PIPEDA, etc.)
- Consider cyber liability insurance that covers data practices
8. Have a Plan B for Account Bans
The reality: If you scrape LinkedIn, account bans are inevitable.
Best practice:
- Don't build your entire prospecting process on scraped data
- Diversify lead sources (conferences, referrals, content marketing)
- Export and back up scraped data regularly
- Have alternative prospecting methods ready
When LinkedIn Scraping Still Makes Sense
Despite the risks, LinkedIn scraping remains common in certain scenarios:
1. One-Time Research Projects
Scenario: Market research requiring industry-specific data collection.
Why it might work:
- Limited scope reduces detection risk
- Research purposes may qualify as "legitimate interest" under GDPR
- Can accept account ban risk for non-recurring use
Recommendation: Use Apify or PhantomBuster for one-off projects with disposable accounts.
2. Competitive Intelligence
Scenario: Tracking competitor hiring patterns, organizational changes, or key employee movements.
Why it might work:
- Public information (company pages, job postings)
- Low-frequency scraping (weekly/monthly)
- Easier to argue legitimate business interest
Recommendation: Use Bright Data with professional legal counsel review.
3. Recruitment at Scale
Scenario: Sourcing hundreds of candidates for multiple open positions.
Why it might work:
- Talent acquisition may qualify under "legitimate interest" (consult lawyer)
- LinkedIn Recruiter Lite offers compliant alternatives
- Some scrapers (e.g., Bright Data) offer recruitment-specific compliance guidance
Recommendation: Explore LinkedIn's official Talent Solutions first; if scraping, use enterprise-grade tools with legal team.
4. When You Have Budget for Legal Risk
Scenario: Enterprise organization with legal counsel, cyber insurance, and risk appetite.
Why it might work:
- Can absorb potential fines and legal fees
- Legal team can document compliance efforts
- Enterprise scrapers (Bright Data) offer some legal support
Recommendation: Full legal review, documented data governance, enterprise-grade tools only.
Frequently Asked Questions
Is LinkedIn scraping illegal?
LinkedIn scraping exists in a legal gray area. The 2020 hiQ Labs v. LinkedIn ruling established that scraping public data doesn't violate the Computer Fraud and Abuse Act (CFAA). However, it does violate LinkedIn's Terms of Service, creating breach of contract liability. Additionally, GDPR and other data privacy laws impose strict requirements on processing personal data—even publicly available information. You can face civil lawsuits, account bans, and GDPR fines up to €20M.
What's the safest LinkedIn scraper tool?
No LinkedIn scraper is truly "safe"—all violate the platform's Terms of Service. That said, Evaboot and Bright Data have better reputations for avoiding detection and offering some legal guidance. The safest approach is to avoid scraping altogether and use compliant alternatives like LeadSpark AI that work with manually collected data.
Can I get banned for using a LinkedIn scraper?
Yes. LinkedIn actively detects and bans accounts using scraping tools. Ban risk varies by tool and usage patterns:
- Low-risk: Occasional manual exports enhanced by external enrichment (Evaboot approach)
- Medium-risk: Browser extensions with rate limiting (Skrapp, Kaspr)
- High-risk: Full automation platforms (PhantomBuster, SalesRobot)
- Very high-risk: Aggressive scraping without delays or stealth features
Expect any scraping account to eventually be banned. Never scrape from your primary professional LinkedIn account.
Is LinkedIn scraping GDPR compliant?
LinkedIn scraping is difficult to make GDPR compliant but not impossible. You must establish a legal basis (usually "legitimate interest"), implement data minimization, provide transparency about collection practices, and honor deletion requests. The CNIL Nestor ruling shows European regulators will penalize non-compliant LinkedIn scraping for B2B prospecting. Consult with legal counsel and document your compliance measures. Consider whether the GDPR risk (fines up to €20M) justifies your scraping use case.
What are ethical alternatives to LinkedIn scraping?
Ethical, compliant alternatives include:
- LeadSpark AI: Works with manually collected data to generate personalized icebreakers without automation
- LinkedIn's official APIs: Limited but fully compliant access to certain data types
- Manual Sales Navigator exports: 2,500 leads per list with basic data fields
- Verified data providers: Purchase compliant B2B contact lists from legitimate vendors
- Content marketing: Attract inbound leads instead of scraping outbound prospects
- Referral programs: Leverage existing customers for warm introductions
How do I avoid getting caught scraping LinkedIn?
To minimize detection risk:
- Limit to 50-100 profile views per day per account
- Add randomized delays (5-15 seconds) between actions
- Mimic human behavior (browse during business hours, not 24/7)
- Use residential proxies (not datacenter IPs)
- Rotate multiple LinkedIn accounts
- Choose "stealth" tools (GiveMeLeads, Bright Data)
- Never scrape from your primary professional account
However, understand that LinkedIn's detection systems improve constantly. Long-term scraping will likely result in bans regardless of precautions.
The Bottom Line: Choose Compliance Over Convenience
LinkedIn scraping tools offer tempting shortcuts for sales prospecting—but the legal risks, account bans, and GDPR penalties make them a dangerous choice in 2026.
Key takeaways:
- ❌ All LinkedIn scrapers violate the platform's Terms of Service without exception
- ⚖️ GDPR fines reach €20M for non-compliant personal data processing
- 🚫 Account bans are inevitable for users of aggressive scraping tools
- ✅ Compliant alternatives exist that deliver better results without legal risk
- 🎯 [LeadSpark AI](/] offers the best of both worlds: LinkedIn-powered personalization with zero compliance risk
The smartest sales teams in 2026 aren't asking "which scraper should I use?"—they're asking "how can I leverage LinkedIn data compliantly?"
Try LeadSpark AI free and see how compliant, AI-powered personalization outperforms risky scraping every time.
Sources:
- GiveMeLeads: Top 27 Best LinkedIn Scrapers in 2026
- Lindy: 10 Best LinkedIn Scrapers for Data Extraction
- Snov.io: Best LinkedIn Scraping Tools and Practical Guidelines
- Evaboot: Top 26 LinkedIn Scraping Tools to Extract Data
- Nubela: Is Professional Social Network Scraping GDPR Compliant?
- PhantomBuster: Is LinkedIn Scraping Legal?
- Dastra: GDPR and Web Scraping: A Legal Practice?
- Scrupp: LinkedIn Scraping Guide - Legality, Ethics & Best Practices
- Medium: A Comprehensive Guide to LinkedIn Scraping - Legality and Ethics
- DataPrixa: Is Email Scraping Legal? The Complete 2026 Guide
Ready to Generate Personalized Icebreakers?
Join sales professionals using LeadSpark AI to create hyper-personalized LinkedIn icebreakers in minutes.